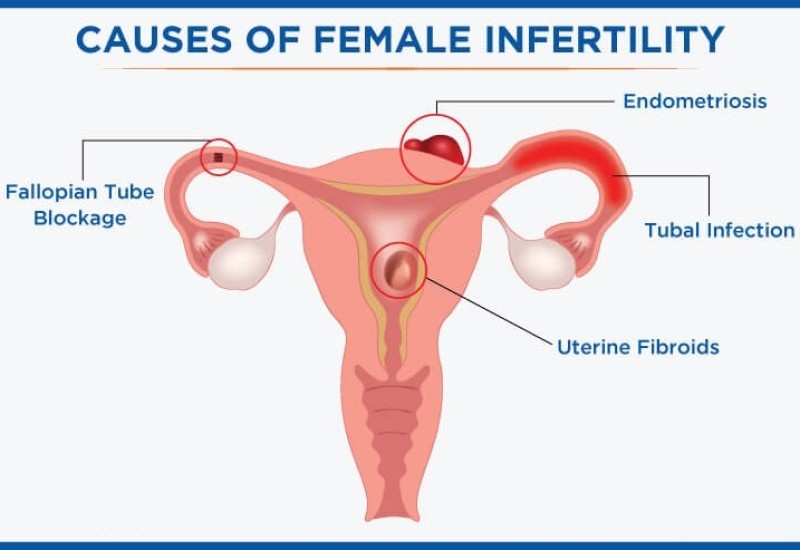
Quality control is critical for bioanalytical laboratories offering solutions such as cell toxicity assay and HPLC testing services to ensure good data comparability. Quality control is a set of techniques or activities where the aim is to ensure that laboratories meet all quality requirements. Ensuring quality requirements requires monitoring processes and solving issues with method performance.
Laboratories have multiple regulatory texts, such as quality assurance assistance and good laboratory practices to perform quality control and assurance in HPLC labs. However, these international recommendations offer only general rules related to quality control. Hence, it’s the laboratory’s responsibility to establish appropriate protocols that ensure high-quality data and method performance. The current article discusses quality control and assurance in HPLC labs.
Ensuring high performance and reliable results through quality control and assurance
The primary step for ensuring high-quality control and assurance is using validated methods that guarantee the fulfillment of all analytical requirements. Generally, method development precedes validation. The second step is monitoring and maintaining assay performance during routine analysis. Analysts are responsible for deciding when the bioanalytical method satisfies all quality criteria and when the generated data can be accepted.
Complete method validation of HPLC assays is time-consuming and may not necessarily be conducted regularly. Researchers often select a few relevant tests to ensure consistent working of the developed method. For example, injecting a calibrated solution of compounds may demonstrate the column performance before routine use. Besides, evaluating the retention times and peak shapes may reveal bad chromatographic separation and suggest maintenance of the HPLC method before continuing sample testing on the instrument.
The required data precision and accuracy should also determine the specifications of an HPLC system. Usually, pharmacokinetic analysis employs three quality control procedures. Reference materials are the most common tools used to prove analytical accuracy. Today, different matrix samples are available from international organizations. However, reference materials may not be easily available and cost more for routine analysis.
The second method to perform quality control is using internal references with known values. This internal reference sample is analyzed with each batch of samples. Internal references are prepared in the laboratory with in-house material. Control charts prepared using data of internal reference help evaluate the quality performance during a specific time and help make rapid modifications in the procedure. Finally, the last method to assess quality performance is to participate in an independent testing scheme. This method includes evaluating laboratory performance by comparing its data with other laboratories.
Several research publications have reported performance qualification of HPLC testing, considering its significance in quality control. Although these publications provide general guidance, they do not have practical application for HPLC quality control and assurance. However, biomedical and environmental literature offers in-depth information on HPLC quality control and assurance. However, these practices differ from one HPLC lab to another, and hence, do not give a comprehensive picture of HPLC quality control and assurance. Therefore, a combined effort from HPLC labs, research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory bodies on quality control and assurance is needed to generate reliable, reproducible, and accurate results.